EnviroMail 09 USA
1,4-dioxane Emerging Contaminant
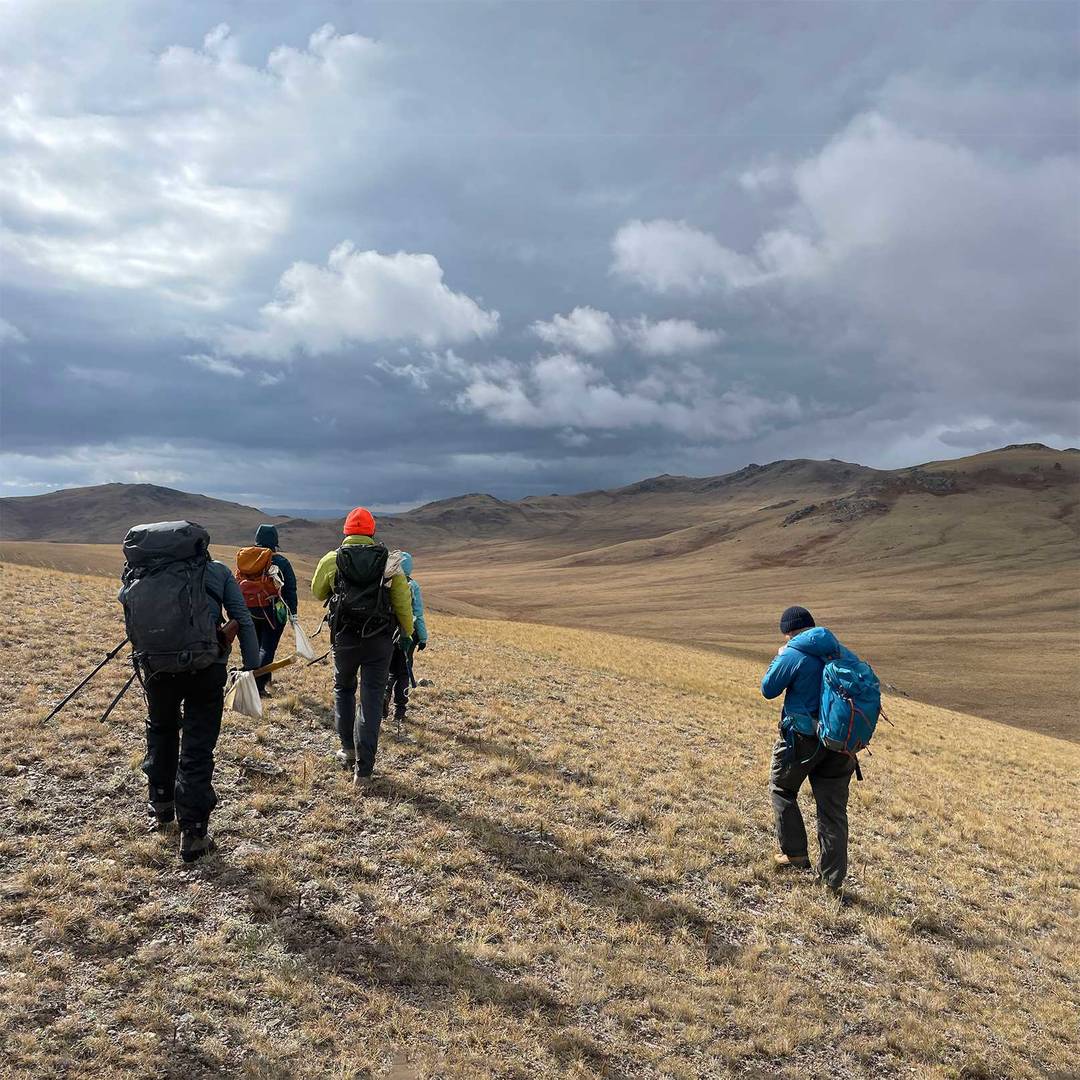
Given 1,4-dioxane’s mobility, a key issue in characterising impacted sites is establishing the extent of migration in groundwater. 1,4-dioxane is not only mobile in the environment but also persistent.
1,4-dioxane is an emerging contaminant of concern. It is highly soluble in water, does not bind to soils and readily leaches to groundwater. Given 1,4-dioxane’s mobility, a key issue in characterising impacted sites is establishing the extent of migration in groundwater.1,4-dioxane is not only mobile in the environment but also persistent.
Uses of 1,4-dioxane
The main application of 1,4-dioxane was as a stabiliser in common solvents such as 1,1,1-trichloroethane. Solvents used in de-greasing, electronics and many other applications may have contained 1,4-dioxane. It is now understood that 1,4-dioxane is widespread in the US due to its use in personal care products and detergents. It can also be found in lacquers, paints and plastics and as an impurity in antifreeze and de-icing fluids.Potential human health and environmental impacts of 1,4-dioxane
1,4-dioxane unique physical and chemical characteristics identified above, make 1,4-dioxane an increasing focus of controlled waters risk assessment. The fate and transport properties of 1,4-dioxane create challenges for investigation, assessment remediation. As such, particular care and experience must be applied to the analysis of 1,4-dioxane in environmental samples. 1,4-dioxane is primarily a contaminant in groundwater. The miscibility and low sorption potential of 1,4-dioxane, allows it to migrate ahead of other contaminants in extended plumes. 1,4-dioxane has a very low octanol water partitioning coefficient (Log Kow of –0.27) and Henry’s constant (4.8 × 10-6). Impacts have been identified at drinking water abstractions and focus globally has be on public water supplies. This mobility and recalcitrance has challenged remediation professionals to redesign existing treatment systems such as air stripping and adsorption to granular activated carbon. It is classified by United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) as likely to be carcinogenic to humans by all routes of exposure and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as a Group 2 probable human carcinogen.
1,4-Dioxane Analysis
ALS can carry out analysis of water samples for 1,4-dioxane by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). The analytical approach adopted increases sensitivity using GC-MS in conjunction with isotope dilution and selective ion monitoring. The limit of reporting (PQL) is 0.07 μg/l.
Samples should be collected in glass bottles (minimum volume: 100 mls). 1,4-dioxane can also be sampled utilizing Rigid Porous Polyethylene (RPP) samplers, reducing labor cost for clients.
Equipment used in sampling can be a source of crosscontamination. 1,4-dioxane also might be present in detergents used for de-contamination purposes. When collecting samples for 1,4-dioxane, submission of additional field and equipment blanks is recommended prior to and during sampling to ensure a robust system of QA/QC is followed.