-
 Rechercher
Rechercher
Search
-
 français
français
-
 Connexion
Connexion
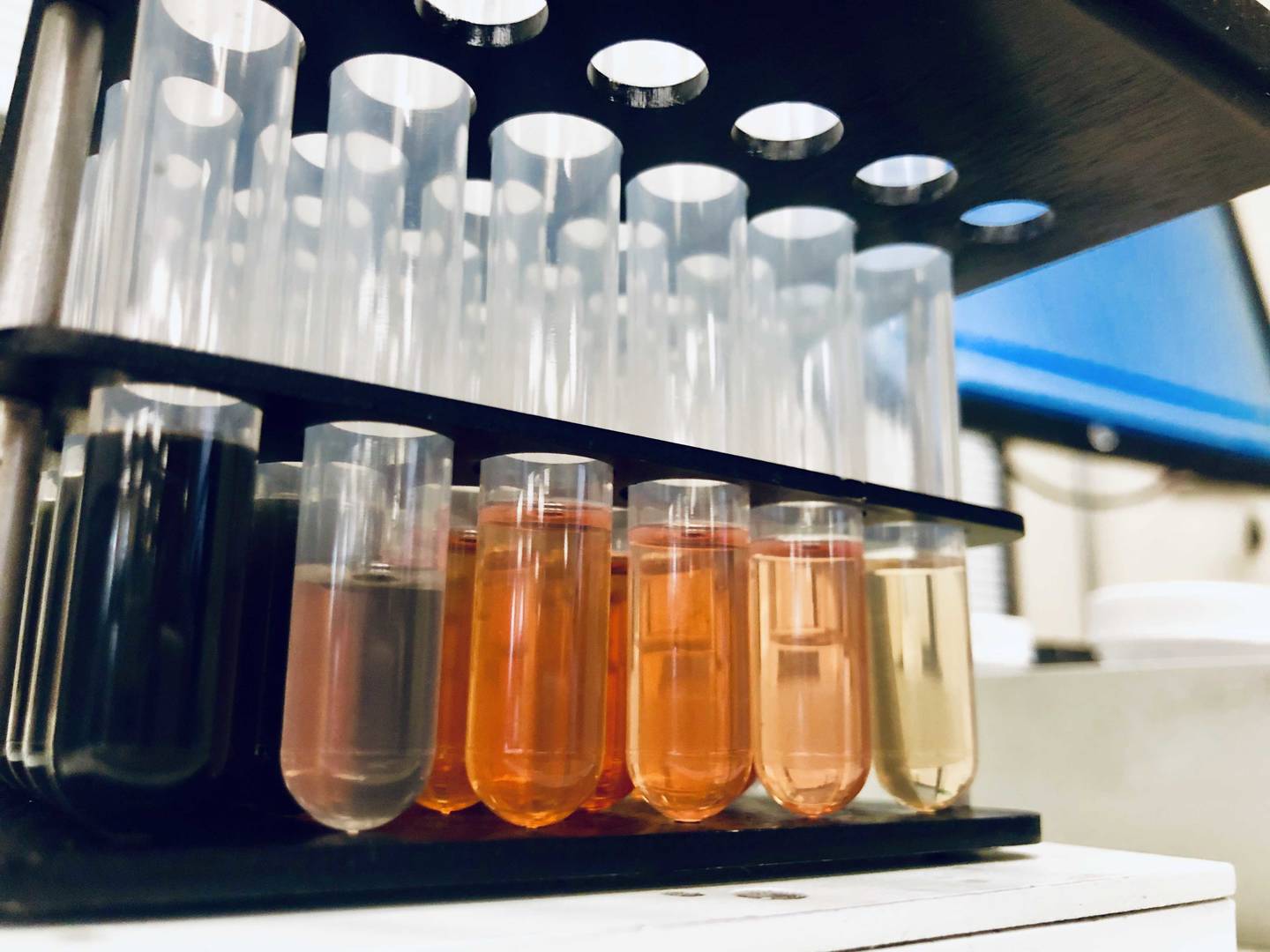
ALS Solutions
ALS Solutions vous fournit un accès en ligne à vos échantillons et à vos informations analytiques, où que vous soyez.
ConnexionGeochemistry WebtrieveTM
Récupérez les résultats et suivez la progression des échantillons en temps réel grâce à l’accès aux produits numériques présentés, tels que CoreViewer™ et ALS QCPro™.
Connexion
Tribology 360
Cette application pratique permet aux clients de suivre de près et en temps réel les rapports d’analyse d’hydrocarbure en cours de traitement.
Connexion